Weight Loss & wellness
Male Bioidentical Hormone Replacement
Male Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT) involves the use of hormones that are structurally identical to the hormones naturally produced by a man’s body. Natural Hormones are essential to healthy, vigorous and more youthful bodily function.
This treatment is available at Aesthetics Concierge of Texas, here you will find everything you need to know about male BHRT.


Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy at Aesthetics Concierge of Texas
What is included in the treatment package:
– Consultation with one of our experts for personalized discussion
– Lab work to understand the intricacies of your unique needs, paving the way for a tailored hormone replacement plan
– Follow up consultation for comprehensive monitoring
🚨 Superbill for insurance submission 🚨
Learn More About Male Bioidentical Hormone Therapy
HORMONES AND LIBIDO WITH DR. JIM HRNCIR
In this video Dr. Jim Hrncir discusses BHRT and libido. Dr. Jim Hrncir works in collaboration with the Board Certified Nurse Practitioners at Re-Gen & Aesthetics Concierge of Texas.
What Is Male Bioidentical Hormone Replacement?
Male Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement is a personalized approach to hormone therapy designed to restore hormonal balance in men. Bio-identical hormones are natural hormones that are essential to healthy, vigorous and more youthful bodily function.
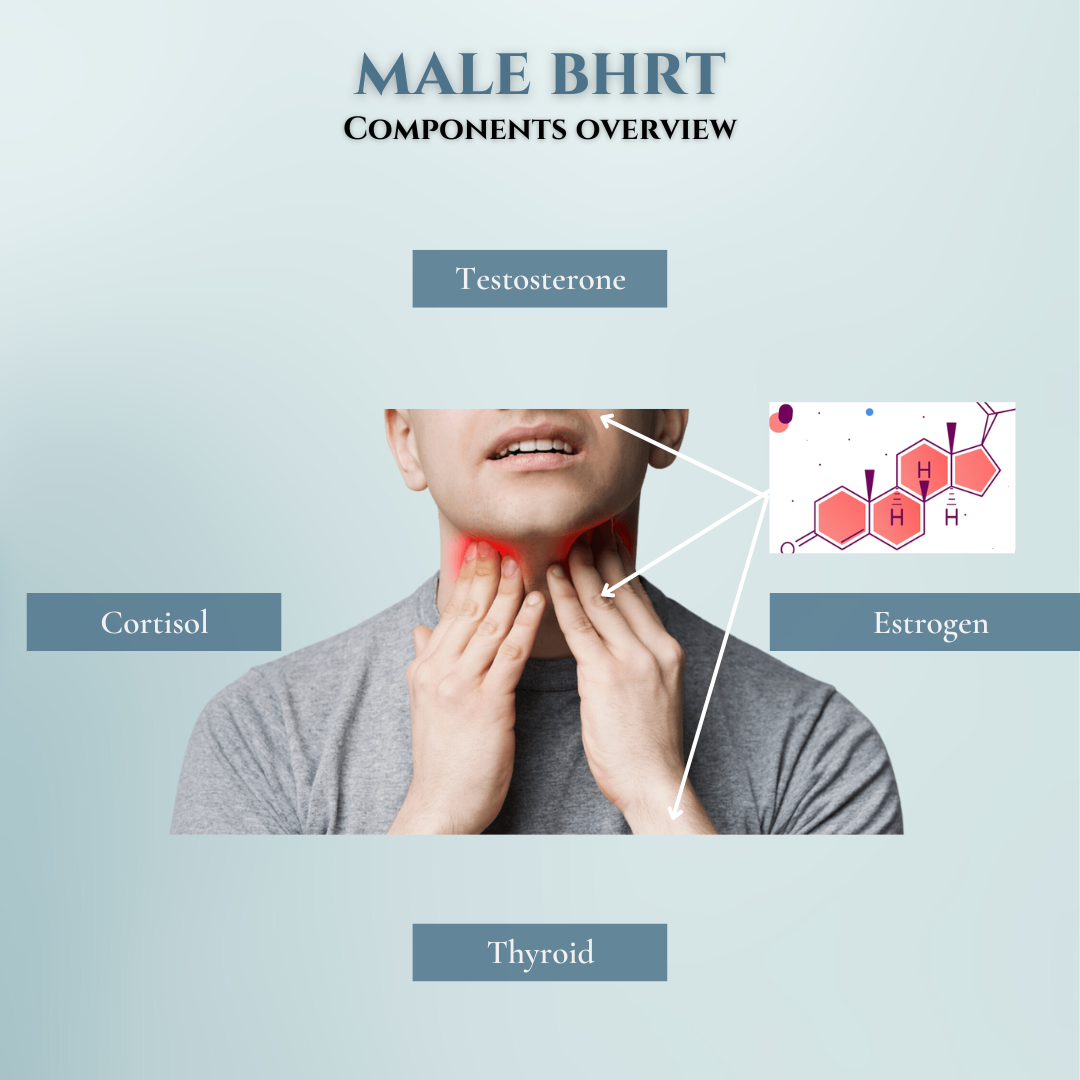
For optimal wellness, men must maintain a proper balance of the natural hormones:
- Testosterone
- Estrogens
- DHEA
- Pregnenolone
- Cortisol
- Thyroid
Natural hormones are derived from plant sources, usually soy or yam, and then modified to become chemically identical to human hormones. Because they are exactly what the human body produces, we refer to these hormones as biologically identical or “Bio-Identical” for short. These “prescription-only” hormones are then used to replace missing or depleted levels in the body.
“Bio-identical” hormones, naturally occurring in the human body, cannot be patented by drug companies and are therefore largely supplied by compounding pharmacies.
This therapy aims to address hormonal imbalances that may occur due to aging, stress, or other factors.
Ready To Book An Appointment?
Ready to schedule your Initial Consultation with our Nurse Practitioners? Click on the link below!
Types of Male Hormone Therapies
Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Testosterone Replacement Therapy, or TRT, is a medical intervention designed to address low testosterone levels in individuals. Testosterone, a crucial hormone for various bodily functions, can decline with age or due to other factors. TRT involves the administration of synthetic or bio-identical testosterone to restore levels, potentially improving energy, libido, muscle mass, and overall well-being. The treatment is personalized based on individual needs and is closely monitored by healthcare professionals.
DHEA Supplementation
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a natural steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands. DHEA supplementation involves taking DHEA in the form of a supplement to address potential deficiencies. DHEA is a precursor to both testosterone and estrogen, and its supplementation may contribute to hormonal balance. It is often considered in personalized hormone plans to support overall health, vitality, and well-being.
Individualized Hormone Plans
Individualized hormone plans are personalized treatment approaches that consider a person’s unique hormonal profile, health goals, and symptoms. These plans may include a combination of interventions, such as hormone replacement therapies, lifestyle modifications, and nutritional support. Healthcare providers tailor these plans to address specific imbalances, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized approach to hormonal health.
Male Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement offers a personalized and holistic approach to hormonal health, aiming to optimize overall wellness and mitigate the effects of hormonal imbalances.
Testosterone: Best Male Bioidentical Hormone
TESTOSTERONE BENEFITS
Tesosterone helps men live longer with better quality of life
Reduces risk of heart attack, stroke, prostate cancer, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, dementia, moodiness/depression, erectile dysfunction, inflammation
Refer to clinical studies and data section
Symptoms of Low Testosterone (LOW T)
Low testosterone levels, commonly referred to as Low T, can have a range of physical, emotional, and mental consequences for men. These consequences may manifest gradually and impact various aspects of daily life. Here’s a brief overview:
Flabbiness or loss of muscle mass
Loss of muscular strength and endurance
Lack of energy and stamina
Decreased sex drive
Loss of motivation and drive
Decreased armpit, pubic, and body hair
Gynecomastia (man breasts)
Erectile dysfunction
Moody or depressed
Cholesterol elevation
Impaired memory and concentration
Indecisiveness
Increased body fat
Loss of coordination and balance
Sleep disturbances or insomnia
Factors That Decrease Testosterone Levels
Understanding the following factors is crucial for identifying potential contributors to low testosterone levels. If individuals experience symptoms of low testosterone, consulting with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance is recommended.
Chronic emotional or physical stress (hypothalamus/pituitary down-regulation)
Aging
High glycemic diet, excess body fat
Prior use/abuse of steroids (shuts down HPG axis)
Increased SHBG (binds testosterone so that it is not bio-available)
Intense physical activity (over-training)
Zinc deficiency, low Vitamin D
Elevated Prolactin (pituitary adenoma)
Traumatic Brain Injury
Medications can lower T levels
Statins
Anti-hypertensives (beta blockers)
SSRI (Prozac)
Corticosteroids (prednisone)
Chronic opiate use (chemically castrates men by suppressing HPG axis)
All About the Thyroid
T4 is the precursor thyroid hormone; HPT axis feedback from T4 levels (increased TSH when low). T3 is the active thyroid hormone.
Symptoms of low thyroid
Fatigue
Weight gain
Loss of out half of eyebrows and unexpected scalp hair loss
Body temperature below 98.2
Cold hands and feet, intolerance to cold
Dry skin, week or ridged nails
Decreased memory and concentration
Puffy eyes and swollen eyelids
Low blood pressure
Depressed mood
Muscle weakness
Headache
Fluid retention
Symptoms of high thyroid
Tachycardia
Heart palpitations
Nervousness/anxiety
Insomnia
Weight loss
Subclinical hypothyroidism
- Subclinical hypothyroidism is associated with a 260% increase in the prevalence of heart disease, atherosclerosis, low metabolism, weight gain, increased auto immune diseases, more inflammatory and chronic pain, increased glandular cancers and cancer mortality
Why do we prescribe Desiccated Thyroid vs. Synthroid/Levothryroxine
Synthroid is a brand name for levothyroxine, a synthetic (man-made) form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine, or T4. NP Thyroid, Armour Thyroid, and W.P Thyroid are brand names for a natural form of thyroid hormone. It is made from the dried thyroid glands of pigs. More than 15% of hypothyroid patients with a normal TSH on Levothyroxine feel hypothyroid. This happens less with patients on desiccated thyroid.
In studies comparing desiccated thyroid with Levothyroxine, patients on desiccated thyroid preferred desiccated thyroid over Levothyroxine.
Levothyroxine contains only T4, while T3 is the active hormone. The body makes 85% T4 and 15% T3. Conventional approaches hope the body goes into over-drive to convert the T4 to T3, but in many patients that doesn’t happen.
Rules when you have your labs drawn:
In AM, fasting
If receiving transdermal, do not apply hormones with hand or to arm of blood draw for 3 days prior to lab draw
Transdermal: draw 24 h after last application
Sub-Q: draw AM of day 3-4 (before next injection)
No Biotin for more than 3 days prior to draw
NO AM meds until after lab draw (including thyroid medication …wait to take all meds until after draw)

Benefits of Male Hormones
Increased Energy and Stamina: Optimization of testosterone levels can contribute to improved energy levels, stamina, and overall vitality.
Enhanced Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone plays a crucial role in supporting muscle development and maintaining lean body mass.
Improved Mood and Mental Clarity: Hormonal balance, especially with testosterone, is linked to mood regulation and cognitive function.
Better Sleep Quality: Hormonal balance can positively impact sleep patterns, leading to improved sleep quality.
Libido and Sexual Function: Restoring testosterone levels can enhance libido, sexual function, and overall sexual well-being.
Male Bioidentical Hormone Replacement FAQ
In this FAQ section, we will answer some common questions about Male BioIdentical Hormone replacement. Whether you’re considering this treatment or just curious about the procedure, this section will provide you with valuable information to help you make an informed decision.
Please reach us at [email protected] if you cannot find an answer to your question.
What is the purpose of Male Bio-Identical Hormone Therapy (BHRT)?
BHRT for men is designed to address symptoms of hormonal imbalance, such as fatigue, decreased libido, and mood swings. It aims to optimize hormone levels using compounds that mimic the molecular structure of hormones naturally produced in the male body.
Who is a suitable candidate for Male BHRT?
Men experiencing symptoms related to age-related hormonal changes, such as low testosterone levels, may be suitable candidates for BHRT. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to assess individual health status and determine eligibility.
Which hormones are typically addressed in Male BHRT?
Male BHRT commonly focuses on optimizing testosterone levels, but it may also involve addressing imbalances in other hormones such as DHEA and thyroid hormones. These hormones play key roles in energy levels, libido, and overall well-being.
What are the potential benefits of Male BHRT?
BHRT for men aims to alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, including increased energy, improved mood, enhanced libido, and better muscle mass maintenance. It may contribute to overall vitality and well-being.
How is Male BHRT administered, and are there different options?
BHRT for men can be administered through various methods, including injections, creams, gels, or pellets. The choice of administration method depends on individual preferences, lifestyle, and treatment goals. A healthcare provider will discuss these options during the consultation.
